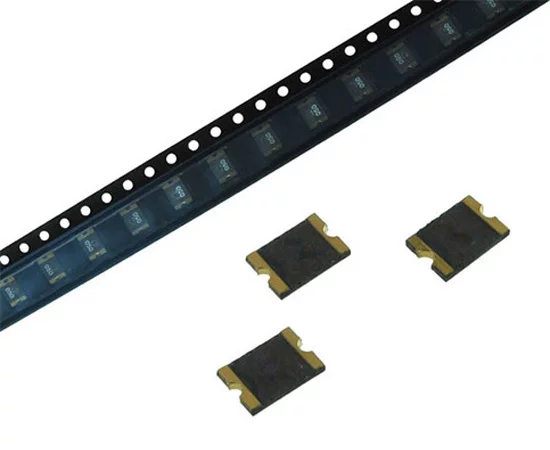
SMD polymer fuses: New technologies in circuit protection
SMD (Surface-Mount Device) polymer fuses are key elements in protecting electronic circuits, specifically designed for surface mounting on printed circuit boards (PCBs). They combine the benefits of polymer fuses with a compact size and ease of installation, making them ideal for use in modern, miniature electronic devices.
What are SMD Polymer Fuses?
SMD polymer fuses are self-resetting overcurrent protection devices designed for surface mounting on PCBs. Utilizing PPTC (Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient) technology, they change their resistance in response to an increase in temperature caused by excessive current flow. Under normal conditions, they act as low-resistance conductors. However, when the current exceeds a certain threshold, the polymer heats up, causing a sharp increase in resistance and limiting the current. Once cooled, they return to a conductive state.
Key Features of SMD Polymer Fuses:
- Compact Size: SMD fuses are very small, allowing for space-saving on PCBs. This makes them ideal for use in modern electronic devices where miniaturization is critical.
- Automatic Resetting: After cooling, SMD fuses reset themselves, allowing for repeated use without the need for replacement.
- Overload Protection: They protect electronic circuits from excessive current flow and short circuits, reducing the risk of component damage.
- Self-Recovery: They have the ability to reset multiple times after the overload is removed, eliminating the need for replacement after each trip. This makes them more economical and practical compared to traditional one-time-use fuses.
- Ease of Installation: As SMD components, they can be automatically mounted on PCBs using SMT (Surface-Mount Technology), speeding up the manufacturing process and reducing assembly costs.
Applications of SMD Polymer Fuses:
- Consumer Electronics: They are used in everyday devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, televisions, and audio equipment. They protect sensitive electronic circuits from damage caused by short circuits or overloads.
- Automotive Industry: They are used in vehicle electronic systems where reliability and durability are crucial. They provide protection against short circuits in control circuits, lighting, infotainment systems, and other circuits.
- Telecommunications: In telecommunication devices like modems, routers, and switches, SMD polymer fuses protect circuits from sudden current surges that may occur due to lightning strikes or other disruptions.
- Medical Equipment: Sensitive medical devices that must operate reliably often use SMD polymer fuses to protect their circuits.
- Aerospace and Defense: Due to their reliability and automatic resetting capability, these fuses are used in aerospace systems where component replacement is difficult or impossible.
If you want to see current stock levels and prices, click on the product symbols.
| SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD0603; current: 0.08A; voltage: 15V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C equivalent: 0ZCM0008FF2G |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.12A; voltage: 60V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.16A; voltage: 30V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C equivalent: 1206L016WR |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.20A; voltage: 24V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.25A; voltage: 24V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.25A; voltage: 30V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.35A; voltage: 13,2V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.35A; voltage: 24V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.35A; voltage: 33V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.50A; voltage: 16V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.50A; voltage: 24V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; equivalent: 0ZCJ0050AF2E |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.50A; voltage: 33V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.75A; voltage: 13,2V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.75A; voltage: 16V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.75A; voltage: 24V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 0.75A; voltage: 33V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 1A; voltage: 13,2V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 1.1A; voltage: 13,2V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C;T |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 1.1A; voltage: 16V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 1.5A; voltage: 13,2V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD1206; current: 1.5A; voltage: 16V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD2920; current: 0.75A; voltage: 60V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; equivalent: 2920L075-60MR |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD2920; current: 2A; voltage: 24V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C equivalents: 2920L200/24DR |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD2920; current: 3A; voltage: 6V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; equivalents: SMD300F-2; FSMD300-2920 |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD2920; current: 4A; voltage: 6V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD2920; current: 4A; voltage: 16V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |
|
|
Resettable fuse; SMD2920; current: 5A; voltage: 6V; operating temperature: -40÷85°C; |